Can Hormones Influence the Growth of Your Hair?
Hormones are chemical messengers that coordinate the activity of cells throughout your body. Your endocrine system (the network of glands that produce and secrete hormones) is essential for all aspects of your health, including hair growth.
Certain hormones like testosterone and estrogen can affect hair loss by contributing to certain conditions such as hypothyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and trichotillomania.
The risk of hair loss is different for males and females. For the latter, hair loss tends to be more diffused and can occur on any part of the scalp, but it may affect only one area or multiple areas of the scalp at once.
Understand How Hair Growth Occurs
Hair growth is a complex process involving many different variables. First of all, it is necessary to understand three distinct phases of hair growth: Anagen, Catagen, and Telogen. Each stage has its biological function, which affects how you can grow your hair faster.
Anagen is the active phase of hair growth. This is when new cells are formed and pushed up to the surface of the skin. This phase can last anywhere from two to six years, depending on your hair type and genetics.
The catagen phase is short—just one or two weeks long. After this phase, you reach the telogen stage, which takes about 100 days to complete. During telogen, old cells at the root of your hair fall out and are replaced by new ones so that you can start the cycle all over again.
This cycle repeats itself throughout your life, but typically hair follicles will stop producing hair after about 15 to 25 years. When this happens, hair loss starts to occur.
Hormones determine the passages of hair growth. However, there is still a need for you to know what kind of hormones control the growth of your hair and prevent balding. Several factors can lead to baldness, such as stress, nutrition, and heredity.
Understand the Role of Different Hormones

Understanding what hormones do and how they influence hair growth can be vital to know why you have specific hair issues. Every person has a unique set of genetics that their parents and ancestors influence. This individual genetic makeup influences which hormones your body produces and how those hormones work within your body.
Hair loss occurs when there is a disruption in three hormones- testosterone, estrogen, and DHT. These hormones are responsible for the growth of your hair, so when the balance shifts, the result is thinning or loss of hair.
The following is a breakdown of the roles played by testosterone, estrogen, and DHT concerning how they affect our hair.
Testosterone
It is the primary male sex hormone found in men's bodies. Most people associate testosterone with a muscular build. However, it is also present in females to a certain extent, although in much smaller quantities. Although testosterone plays an essential role in hair growth, it does not seem as crucial as DHT. This is because male pattern baldness does not affect females, nor testosterone directly affects female pattern baldness.
Estrogen
It is the primary female sex hormone responsible for the development of body hair. As we age, our estradiol levels decrease, leading to thinning hairline on the top of the head or frontotemporal recession and general thinning of hair all over.
DHT
DHT or dihydrotestosterone is an essential hormone for hair growth and is produced in the adrenal cortex. In humans, this hormone peaks during adolescence and early adulthood, and then it decreases with age. It is essential in male pattern baldness because it influences how much testosterone they produce.
The more testosterone, the more influence on DHT, which causes hair loss. DHTs build up on the scalp causing thinning hair and eventually leading to baldness which could be very difficult to control. Women can experience the effects of excessive DHT production due to hormonal imbalances or because of other medical conditions like PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome).
Signs of Hormone Fluctuations in Men and Women

The most common hormone-related problems include depression, excess facial hair in women, and loss of hair in men due to various reasons like heredity factors. Hormonal imbalance leads to erratic moods, hair thinning, balding, aggressive nature, depressive episodes, fatigue, etc.
Know the Link Between Menopause and PCOS With Hairfall
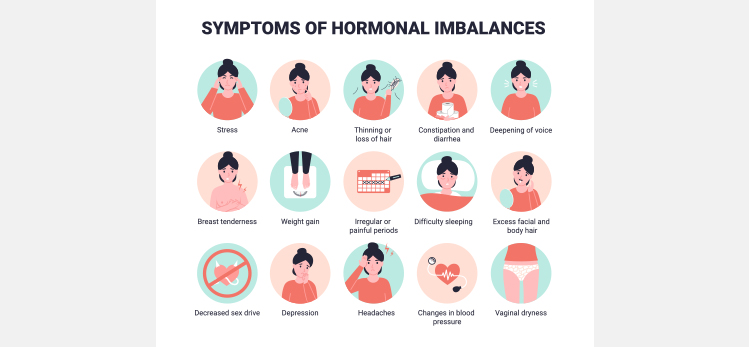
Women with PCOS usually experience excessive hair growth on their face and body in addition to thinning and balding in the scalp.
This is because they have high levels of male hormones called androgens in their body. The ovaries produce these hormones in polycystic ovaries, and when there is an imbalance, it can increase facial and body hair growth.
Every woman experiences hormonal changes throughout her life. Still, women going through menopause tend to be particularly vulnerable when it comes to hormonal changes that affect the growth of their hair.
In addition to experiencing changes in their menstrual cycles, many women also undergo an increase in thinning and balding when they go through menopause. Hence, it is vital to use products that help fight thinning and balding.
Treatment for Hair Loss

To treat hormonal imbalance, certain medications are prescribed by the treating physician that help bring hormone levels back to normal. This is particularly true for women who are going through menopause or who have an underactive thyroid gland.
At times, hormones can be used to reduce severe symptoms of hormonal imbalance. It's important to consult your doctor before taking hormone replacement therapies.
Here are specific methods on how to curb hair loss and regulate hair growth:
Specific surgical methods can also be used to treat this problem effectively. In some cases, laser treatment may be required to stimulate the hair follicles which have become inactive due to hormonal imbalance. This method provides long-lasting results and prevents further hair loss from occurring.
Another treatment option is Minoxidil, which has been shown to help slow down the loss of hair in men and women suffering from Androgenetic Alopecia. It works by widening blood vessels in the scalp, stimulating healthy scalp tissue, and encouraging new hair growth. While taking Minoxidil, please ensure that it is as per the dermatologist’s advice and recommendation only.
In recent years, finasteride has been used primarily as a treatment for male pattern hair loss, a condition that causes the hair on the scalp to recede. Finasteride is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor. It prevents the conversion of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is primarily responsible for causing male pattern baldness and prostate enlargement.
A hair transplant is one of the most effective ways to treat hair loss. While transplants aren't for everyone, they can be an excellent option for men and women looking for a full head of hair.
Regenerative treatments use scalp injections to promote regrowth rather than stimulate dormant follicles as with traditional transplants. Injections contain the platelet-rich plasma, which contains growth factors drawn from the patient's blood.
Conclusion
Find out how your body change can have an impact on your hair by consulting an expert doctor. Master the basics about your body's hormones involving the growth of your hair. Maintaining a healthy and stress-free lifestyle and nutritious meals are also very important for optimal hair care
Myth Busters HairFall

Androgenetic Alopecia - Everything You Need To Know
Have you been experiencing excessive hair fall over a prolonged period of time? It could be an early sign of androgenetic alopecia. It is a hair loss disorder common in both genders and can lead to progressive thinning and even baldness in some patients if not caught and treated early.

How To Make Hair Grow Faster For Men
A head full of healthy hair is a matter of confidence. Hair has its own mechanism of growing and shedding, and it is when this mechanism is thrown off that growth is hindered. Especially in the case of males, hair growth faces a lot of hiccups that can easily be managed.

Female Pattern Baldness - Causes & Treatments
Have you suddenly noticed an increase in the number of hair strands on your pillow in the morning? Or is your ponytail getting thinner by day? Well, you might be suffering from female pattern baldness. While that does sound scary, identifying it early on is key to treating this condition effectively. So keep reading to know what this is, how you can identify it, and most importantly, what treatments you can avail of to get your beautiful lustrous hair back.

What Are The Reasons For Hairfall?
Almost everyone experiences some amount of hair thinning over the years. Shedding around 50 to 100 single strands of hair per day is considered normal. However, losing more than 150 strands a day, experiencing sudden thinning, or developing circular bald patches on your scalp are reasons for concern. Hair loss occurs when new hair doesn’t grow fast enough to replace the amount of hair you lose daily. Hair can fall due to various reasons, with hereditary hair loss and poor nutrition being the most common hair fall reasons.

Expert Approved Tips For Hair Growth
What can be more debilitating than seeing hundreds of hair strands shedding from your scalp every time you brush your hair? Also, excessive molting occurs during seasonal changes that can be very stressful for you. Although it’s okay to lose between 50-100 strands every day, according to the American Academy of Dermatology, the problem occurs when you start shedding more than normal. But that doesn’t mean you have to feel helpless as there are ways to grow your hair back. Even if you are coping with baldness or alopecia, certain hair growth tips from dermatologists can come to your rescue. Read on to discover how these tips can be your savior when abnormal hair fall problems are in sight.
Trending Videos
+ 8 Sources
LMRC - GGI-CO-A2-DMA-300026127-300026127-WM-J21-282
© 2021 Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd. All rights reserved.